Client SSD vs Enterprise SSD – What’s the Difference?
Client SSD vs Enterprise SSD – What’s the Difference?
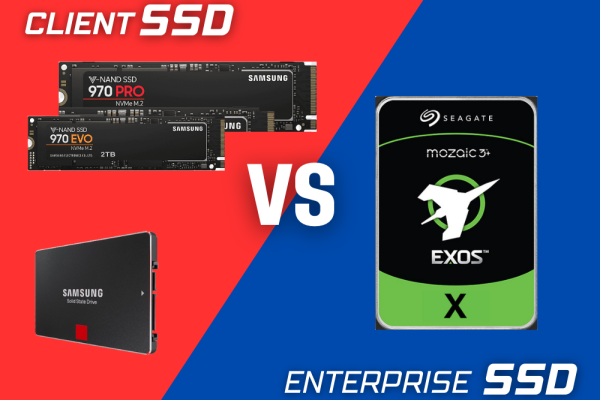
As solid-state drives (SSDs) have become more widespread, their role in both consumer and business environments has grown dramatically. However, not all SSDs are created equal. There’s a major distinction between Client SSDs and Enterprise SSDs, two categories designed for different workloads and performance requirements. Let’s dive into the key differences that set them apart.
1. Performance and Endurance
One of the most significant differences between client SSDs and enterprise SSDs is performance and endurance.
- Client SSDs are optimized for everyday consumer use—think personal computers, gaming systems, and office work. These SSDs are designed for read-heavy tasks such as loading applications, starting operating systems, and moderate file transfers. While they offer fast performance for these types of tasks, they’re not built for handling constant heavy-duty operations.
- Enterprise SSDs, on the other hand, are designed to meet the demands of data centers, servers, and cloud computing environments. These SSDs are engineered for both high read and write cycles, supporting sustained performance over extended periods. They must withstand 24/7 operations and continuous data-heavy tasks such as virtualization, database processing, and large-scale analytics.
2. Durability and Lifespan
Durability is another crucial factor.
- Client SSDs typically offer a lifespan suitable for personal use—lasting anywhere from 3 to 5 years, depending on usage patterns. They use less expensive NAND technology, such as TLC (Triple-Level Cell) or QLC (Quad-Level Cell), which increases storage capacity but reduces write endurance.
- Enterprise SSDs are built with more durable components like MLC (Multi-Level Cell) or SLC (Single-Level Cell) NAND technology, giving them a longer lifespan, often rated to last 5 to 10 years. They also include power loss protection and more robust error correction codes (ECC) to safeguard against data corruption during unexpected failures.
3. Workload Optimization
- Client SSDs are optimized for sequential workloads, which means they are designed to handle data in a sequential order, such as loading large media files or booting an OS.
- Enterprise SSDs, however, are built for random workloads. In an enterprise environment, servers are typically handling thousands of requests per second from multiple users, making random read/write performance critical. These SSDs are designed to sustain high IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) over time.
4. Power Loss Protection
One of the key differentiators is how each type handles sudden power loss.
- Client SSDs often lack power loss protection. While some models offer basic protection, most consumer drives rely on the system’s power supply to remain stable during data writing.
- Enterprise SSDs, on the other hand, feature capacitors and other components that ensure data integrity even during a sudden power outage. This is crucial for businesses where downtime or data loss can result in financial or operational setbacks.
5. Cost
Naturally, with the added durability, endurance, and specialized features, enterprise SSDs come with a higher price tag.
- Client SSDs are relatively affordable, making them ideal for consumers who need fast storage at a lower price point. For typical users, these SSDs provide plenty of performance for their needs without the added cost of features they won’t utilize.
- Enterprise SSDs, due to their high-endurance components, better performance, and added features, are more expensive. However, for businesses handling critical operations, the added cost is justified by the reliability and long-term savings due to fewer drive replacements.
6. Reliability and Data Integrity
Data integrity is a priority in business environments where even minor data corruption can lead to significant losses.
- Client SSDs provide basic error-correcting features, but they may not always guarantee 100% data protection, especially in extreme workloads or environments.
- Enterprise SSDs feature advanced ECC algorithms, end-to-end data protection, and data path protection that prevent data corruption during intense, continuous workloads.
Conclusion
When it comes to choosing between a client SSD and an enterprise SSD, it all boils down to your specific needs. If you’re an average consumer looking for faster boot times, quicker application loads, and improved overall performance, a client SSD will serve you well. However, for businesses running critical applications, databases, or cloud services that require constant uptime and high reliability, investing in enterprise-grade SSDs is essential.
Posted 1 year ago
by Armaan